
GIS interoperability is the ability for a platform to read and render multitude spatial data formats, from local sources and from remote public and private datasets via shared open standards. The potential to access spatial data is a common and foremost attribute of NASA World Wind. The purpose of this technology has always been for developers to implement new functionalities and advance existing ones to create increasingly more useful tools for analysis and visualization of Earth and space data. NASA World Wind has been available as open source since 2003 in C#, since 2006 in Java, since 2012 in Android, since 2013 in iOS and since 2014 in JavaScript. 1) allowing users to implement their own model in NASA World Wind. Custom elevation grids can also be uploaded (Fig. the scale of the view determines the detail of the elevation grid. NASA World Wind loads elevation data automatically with a multi-resolution approach, i.e. It provides information not only regarding elevation, but also allows one to derive other morphological features, such as slope, aspect, with the ability to model these dynamics of a planet’s system processes– e.g. A DTM is the digital representation of the elevation of a planet’s surface at ground level. The base model is a virtual globe, a 3D representation of a planet, enriched with its digital terrain model (DTM).
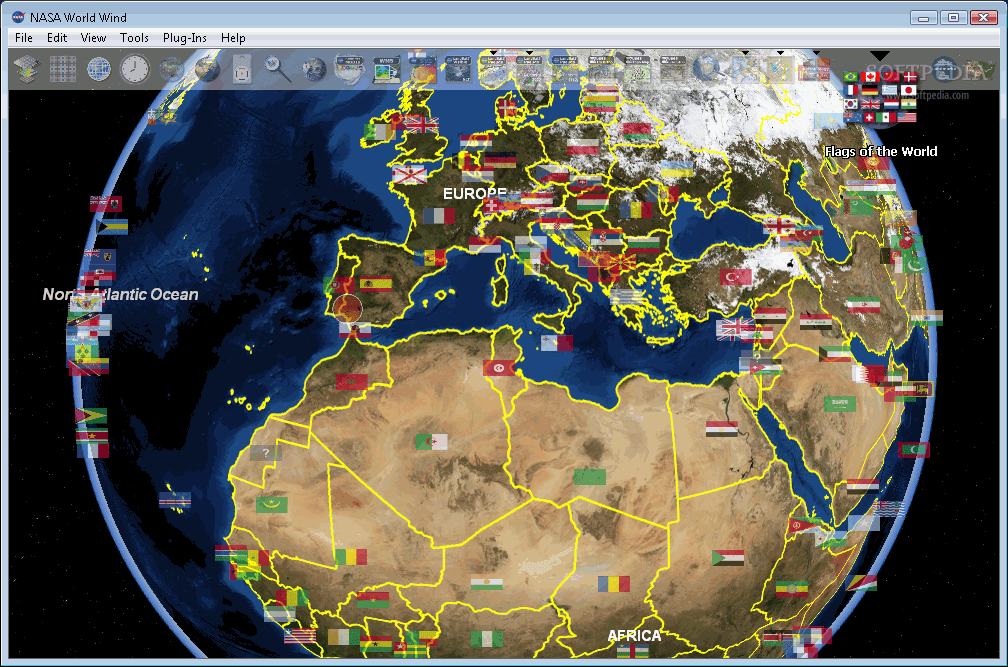
This visualization technology provides a multi-dimensional geographic information system (GIS) and an extensible framework for analyses and visualization of scientific data.
#Parse geojson nasa world wind software
World Wind is an API-centric SDK, an Application Programming Interface (API) Software Development Kit (SDK) that delivers virtual world for experiencing geospatial data in its native context. This motto is fully realized in NASA World Wind. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) was born in 1958 with a motto: “For the Benefit of All”. With this contribution, we want to increase awareness of NASA World Wind as a unique opportunity to foster collaboration between scientists, developers and other stakeholders, enriching knowledge of our Earth’s complexity. The European Space Agency is now partnering with NASA on development of the "ESA-NASA Web World Wind" this high degree of interest from other agencies will boost future project productivity. We give here an overview of the project, reporting details regarding current development direction, with state of the art examples. NASA World Wind provides the ideal environment for scientific data, their analysis, visual representation and interaction with users, in a single platform, which can be deployed both as a Java desktop application (NASA World Wind) or a JavaScript web application (ESA-NASA Web World Wind).
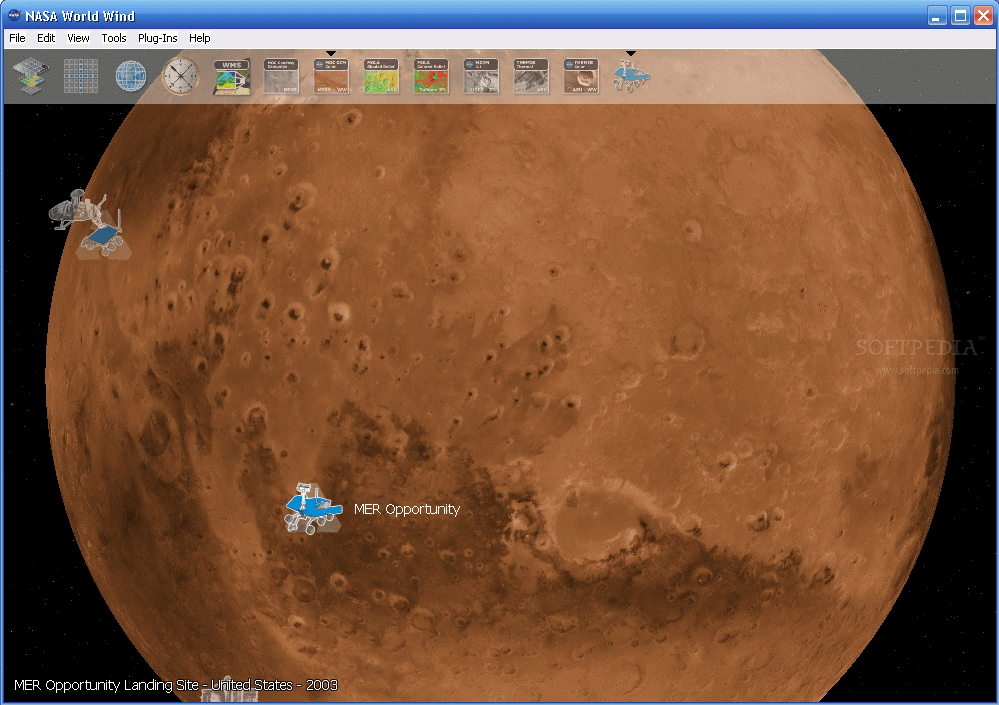
NASA World Wind is an open source application-programming interface for developing geographic information systems based on a virtual globe rendering engine representing a planet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
